# 1、Vuex 是什么?
适用场景: 复杂关系的组件数据传递
Vuex作用相当于一个用来存储共享变量的容器
state用来存放共享变量的地方getter,可以增加一个getter派生状态,(相当于store中的计算属性),用来获得共享变量的值- Vue
actions也是用来存放修改state的方法,不过action是在mutations的基础上进行。常用来做一些异步操作
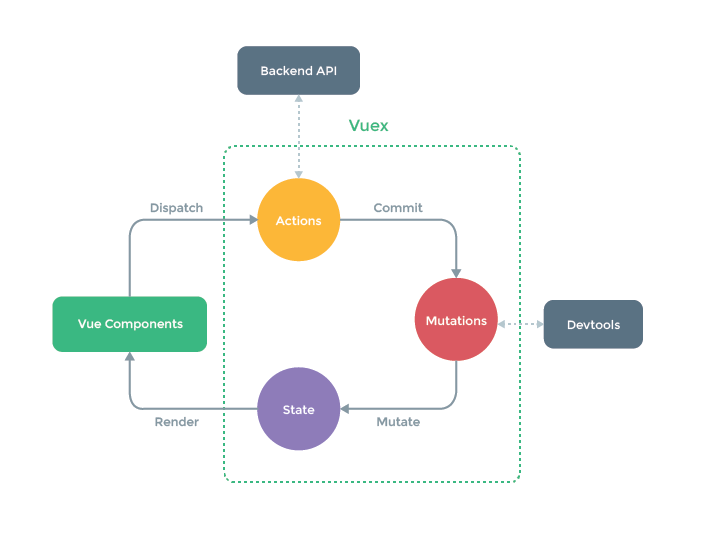
# 2、Store 的实例化过程
State 提供了唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到Store 的 State中进行存储。
// 创建store数据源,提供唯一的公共数据
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// state 指向一个对象, 对象中的数据就是需要全局共享的数据
state: { count:0 }
})
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
- 组件访问State 中数据的两种方式:
// 第一种
$store.state.count(全局数据名称)
1
2
2
// 第二种,从 vuex 中按需导入 mapState 函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
// 将全局数据,映射为当前组件的计算属性
computed: {
...mapState(['count'])
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# 3、什么是单项数据流?
数据触发视图的更改,视图跟用户进行交互,触发动作后修改data数据,整个环形的数据流动就叫做单项数据流。相当于(父组件传入到子组件的过程)
new Vue({
// state 驱动应用的数据源;
data () {
return {
count: 0
}
},
// view 以声明方式将 state 映射到视图;
template: `
<div>{{ count }}</div>
`,
// actions 响应在 view 上的用户输入导致的状态变化。
methods: {
increment () {
this.count++
}
}
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 4、什么是Mutation?
①更改 Vuex 的 store 中的状态的唯一方法;
②只能通过mutation变更 Store数据,不可直接操作 Store 中的数据;
// 定义 Mutation
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count:0
},
mutations: {
addN(state, step){
// 变更状态
state.count += step
}
}
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// 触发 mutation
methods: {
handle(){
// 触发 mutations 的第一种方式
// this.$store.commit('add')
// 调用 commit 函数,触发 mutations 时携带参数
this.$store.commit('addN', 3)
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
总结: store 就是一个数据仓库,为了更方便的管理仓库,把一个大的store拆成小的 modules ;
整个 moudles 是一个树形结构,每个module又分别定义了 state,getters,mutations,actions;
通过递归便利模块的方式,完成了他们的初始化。
Vuex 提供这些API都是方便对store做各种操作来完成各种能力,尤其是 mapXXX 的设计。
