1.Vue是怎么识别 v- 指令的?
首先将HTML结构解析成属性列表,存入到数组中,接着遍历数组中的每一个节点,获取到不同指令对应的方法。
// 将HTML看作真正的属性列表
var ndoeAttrs = node.attributes;
var self = this;
// 类数组对象变为数组,一层一层的遍历节点
[].slice.call(nodeAttes).forEach(attr => {
// 这里开始分析指令
var attrName = attr.name;
var value = attr.value;
// 指令都是 v- 开头的
var dir = attrName.substring(2);
if(attrName.indexOf('v-') == 0){
// v-下不同的指令
if(dir == 'model'){
// console.log('发现了model指令',value);
// 添加Watcher
new Watcher(self.$vue, value, value => {
node.value = value;
});
// 得到 v 的值
var v = self.getVueVal(self.$vue, value);
// 显示 v 的值
node.value = v;
// 添加监听事件,基本实现双向绑定
node.addEventListener('input', e => {
var newVal = e.target.value;
self.setVueVal(self.$vue, value, newVal);
v = newVal;
});
}else if(dir == 'if'){
// console.log('发现了if指令',value);
}
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
2.v-model底层是怎么实现的?
v-model会把关联的相应式数据(info.message),动态的绑定到表单元素的value属性上,然后监听input事件;当
v-model绑定的相应数据发生变化时,表单元素的value值也会随之变化。
<template>
<div>
<div class="message">{{ info.message }}</div>
<div><input v-model="info.message" type="text"></div>
<button @click="change">click</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
info: {}
}
},
methods: {
change () {
this.info.message = 'hello world'
}
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
面试题:v-for 和 v-if为什么不能一起用?
涉及到一个优先级的问题,v-for 比 v-if优先执行,如果一起使用,循环出来的每一项都会去判断一下v-if是否为true或者false,这样就会照成资源的浪费!
3.生命周期
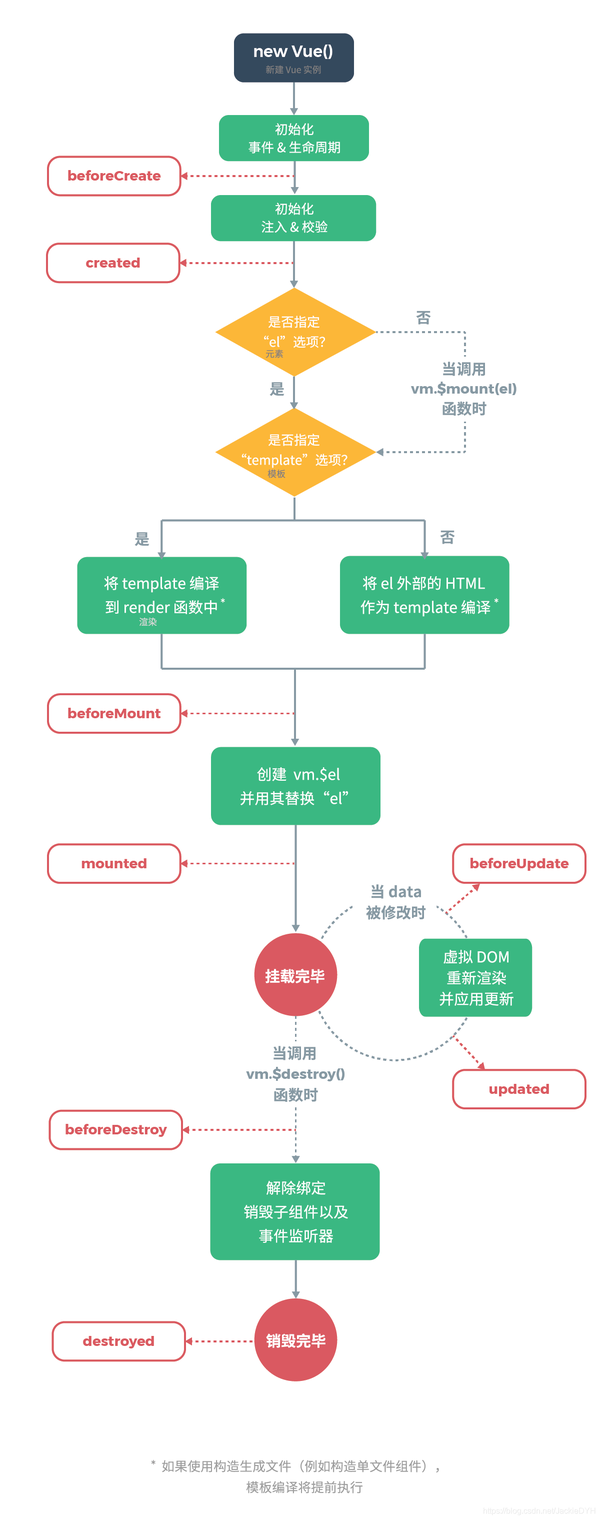

beforeCreate & created
属于实例化阶段,在
_init方法内,DOM 被挂载时执行,两个函数都不能获取到 prop、data 中定义的值,也不能调用methods中定义的函数。
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
// ...
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // 在prop、data 之前解决注入
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // 解决初始化之后的prop、data
callHook(vm, 'created')
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
beforeMount &mounted
属于挂载阶段,在
mountComponent方法内,响应数据被修改时执行,对于同步渲染的子组件而言,mounted钩子函数的执行顺序是先子后父。
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
const name = vm._name
const id = vm._uid
const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}`
const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}`
mark(startTag)
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
// 执行vm._update 把 VNode 渲染到 真实 DOM
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// 把它设为vm._watcher 在watcher的构造函数中.
// 因为观察者的初始补丁可能会调用$forceUpdate(例如:inside child . exe)
// 组件的挂载钩子),依赖于vm._watcher已经定义.
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// 手动挂载实例,调用挂载在self上
// 挂载在其插入的钩子中为渲染创建的子组件调用
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
beforeUpdate & updated
属于更新阶段,在渲染
Watcher的 before 函数内,元素被销毁之前执行,在callUpdatedHooks函数中,等vm._watcher的回调执行完毕后,才能执行update函数。
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
// ...
// 把它设为vm._watcher 在watcher的构造函数中.
// 因为观察者的初始补丁可能会调用$forceUpdate(例如:inside child . exe)
// 组件的挂载钩子),依赖于vm。_watcher已经定义.
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
// ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
beforeDestory & destroyed (3.x中更名为 beforeUnmount & unmounted)
属于销毁阶段,在
$destroy函数前执行,从parent的$children中删掉自身,删除watcher。
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {
const vm: Component = this
if (vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
return
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy')
vm._isBeingDestroyed = true
// 将self从父节点移除
const parent = vm.$parent
if (parent && !parent._isBeingDestroyed && !vm.$options.abstract) {
remove(parent.$children, vm)
}
// 卸载 watchers
if (vm._watcher) {
vm._watcher.teardown()
}
let i = vm._watchers.length
while (i--) {
vm._watchers[i].teardown()
}
// 从数据ob中移除引用
// frozen object 没有观察者。
if (vm._data.__ob__) {
vm._data.__ob__.vmCount--
}
// 调用最后一个钩子
vm._isDestroyed = true
// 在当前redered 树上调用销毁钩子
vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null)
// 销毁钩子函数
callHook(vm, 'destroyed')
// 关闭所有实例侦听器。
vm.$off()
// 删除vue reference
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = null
}
// 发布循环引用
if (vm.$vnode) {
vm.$vnode.parent = null
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
renderTracked & renderTriggered(3.x新增)
都是跟踪虚拟DOM 重新渲染时调用,接收
debugger event参数;renderTracked() : 此事件告诉你哪个操作跟踪了
组件,以及该操作的目标对象和键。renderTriggered() : 此事件告诉你哪个操作触发了
重新渲染,以及该操作的目标对象和键。
<div id="app">
<button v-on:click="addToCart">Add to cart</button>
<p>Cart({{ cart }})</p>
</div>
2
3
4
const app = Vue.vreateApp({
data(){
return{
cart: 0
}
},
// cart 操作*跟踪*了 组件
renderTracked({ key, target, type }){
console.log({ key, target, type })
/*{ key: "cart", target:{cart: 0}, type: "get" }*/
},
// cart 操作*触发*了 重新渲染
renderTriggered({ key, target, type }) {
console.log({ key, target, type })
},
methods: {
addToCart(){
this.cart += 1
/*{ key: "cart", target:{cart:1}, type: "set" }*/
}
}
})
app.mount('#app')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
总结: Vue生命周期函数就是在初始化,及数据更新过程各个阶段执行不同的钩子函数;在created钩子函数中可以访问到数据,在mounted钩子函数中可以访问到DOM,在destroyed 钩子函数中可以做一些定时器销毁工作!
参考:v-model源码解析
s
